Authors
Jason R Sinner, Linda R Greer, Denise M Reddy, Matthew McCabe, Leeann D Louis, Christoph I Lee, Diana S Buist, Edgar A Wakelin, Bryan Haslam
Purpose
Screening mammography volumes continue to increase while radiologist availability remains limited, creating workflow challenges that can lead to fatigue and burnout. Through a radiologist-industry collaboration, an Efficient Clickable Reporting Tool (ECRT) was co-developed to address reporting inefficiencies identified by practicing radiologists. This study evaluates the real-world impact of this collaboration on mammography read times following large-scale clinical deployment.
Materials and Methods
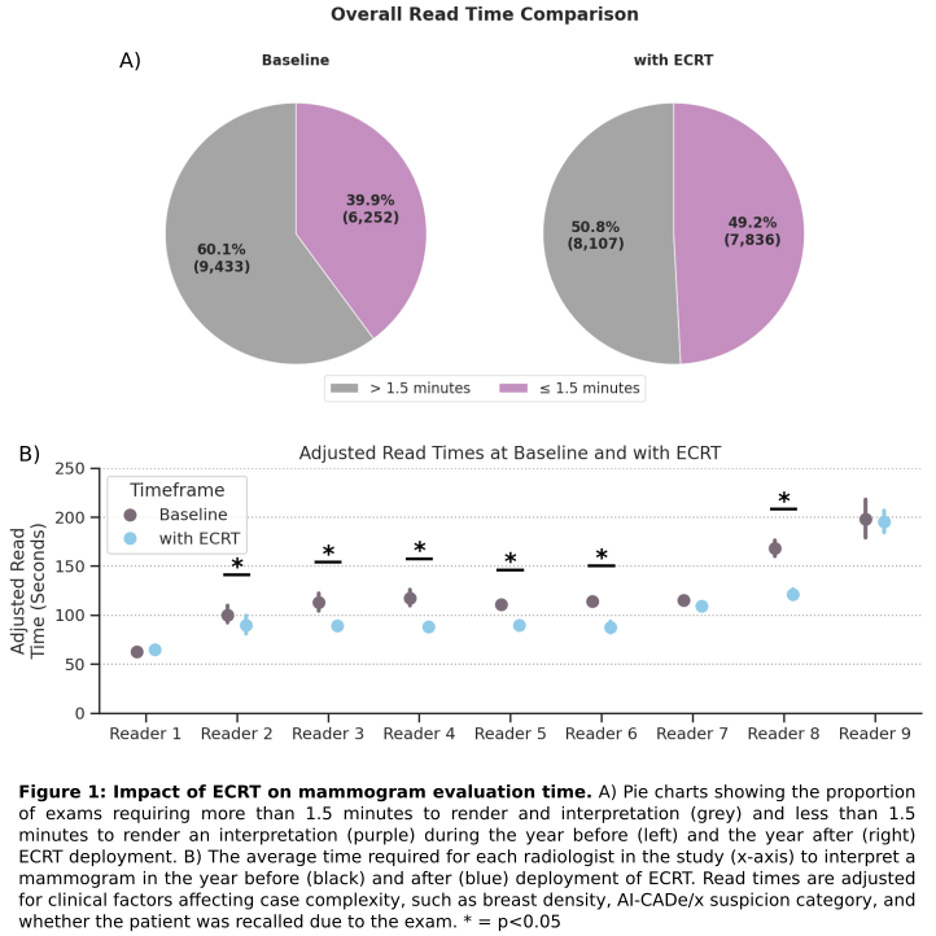
The ECRT emerged from radiologist-identified workflow pain points and was refined through iterative industry collaboration to create a standardized clickable interface with keypad shortcuts, eliminating dictation dependency. The tool was originally developed at a radiology practice in Maryland, and was then deployed across 12 Arizona imaging facilities to rigorously assess its impact on radiologists in clinical practice. Read times were measured before (Aug 2023-Aug 2024, n=15,685 exams) and after (Sept 2024-July 2025, n=15,943 exams) implementation. Analysis included 9 radiologists reading >100 mammograms in both periods. Read times were calculated as intervals between consecutive exam signings, excluding <5 seconds or >5 minutes. Because read times are not normally distributed, a Generalized Linear Mixed Effects Model was used to assess the statistical significance of read time reduction before and after ECRT deployment while adjusting for radiologist variability and clinical case complexity factors including breast density, AI cancer suspicion levels, and recalls.
Results
Post-ECRT deployment, the proportion of exams requiring less than 1.5 minutes to review and interpret increased from 39.9% to 49.2%. Model-adjusted results indicate ECRT significantly reduced read times by an average of 16% (95% CI: 5-26%, p=0.003). Additionally, 6 out of 9 radiologists improved significantly, with individual read-time reductions ranging from 5% to 28%.
Conclusion
Radiologist-industry collaboration successfully translated clinical workflow insights into a deployed technology solution, achieving measurable efficiency improvements. The partnership model enabled rapid iteration from concept to validated clinical tool with demonstrable real-world impact.
Clinical Relevance
Radiologist-driven innovation combined with industry development capabilities can address pressing workflow challenges at scale such as efficiency gains to support sustainable screening mammography capacity as population demands increase.